The field of orthodontics has improved by leaps and bounds thanks to 3D printing. With an intraoral scanner, dental modeling software, and a dental 3D printer, orthodontists can get ahold of precisely fabricated oral appliances, including braces.
This gives them more control over tooth movement and more effective results. Most of all, 3D printing in dentistry allows for faster and more affordable manufacturing of oral appliances. Orthodontists and other dental professionals can also use 3D printing to make custom tools, dental implants, dental crowns, dentures, and more.
However, even as the dental 3D printing industry grows, few people understand biocompatible resins and their contributions to the success of 3D orthodontics and dental work. What are they and how do they work?
The Safe Type of Resin
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) uses the term biocompatible to describe a medical device or item that passed a series of tests according to ISO standards, assuring the public of its safety and effectiveness for its intended use. These tests are designed to answer whether a product will harm the people who use it.
The right resin material is necessary for printing effective and safe orthodontic appliances and other dental objects. Bonding trays, splints, bases, and others must be printed using biocompatible resins. Without biocompatible materials, 3D printed appliances are likely to do more harm than good. FormLabs, Stratasys, and Envisiontec are three of the biggest names that manufacture and supply such resins to dental practices and orthodontics clinics.
Biocompatible 3D printing resins must undergo biologic evaluation (testing for cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, delayed hypersensitivity, and more.
From Dental Molds to Dental Appliances
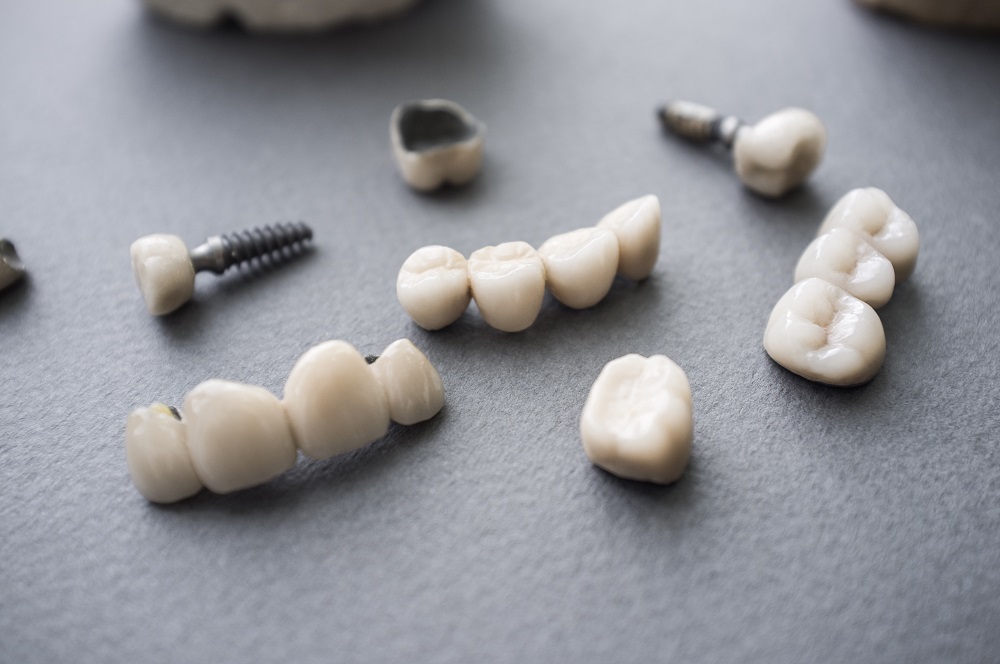
Not all biocompatible resins are made equal. Choosing the right type of biocompatible resin for the job depends on how the product will be used. Moreover, using the right printing materials for certain models or dental appliances may improve its effectiveness. The different types of biocompatible printing materials include:
- PEEK (polyether ether ketone) polymer
- ULTEM (an amorphous thermoplastic polyetherimide)
- SLA (stereolithography apparatus) resins
- PolyJet Resins
- Cobalt chromium
- Titanium
Printing 3D indirect bonding trays and occlusal splints require clear, rigid biocompatible resins. Flexible resins can reduce the accuracy of bonding trays and make the seating of the tray less predictable. The minimum resolution requirement for direct-printed appliances (or those that don’t use a physical model) is 100 microns. Some biocompatible resins are designed for even higher printing resolutions.
Biocompatible resins and high printing resolutions aren’t necessary for dental models. Although you can use such materials and printing settings, take note that higher resolutions take more time to print. Opaque materials are recommended for printing orthodontic models, so fine details are more easily visible.
Continuous Innovation and New Materials
Manufacturers continue to experiment and produce new biocompatible 3D printing materials to improve dental appliances and other medical devices.
For instance, 3Dresyns, a manufacturer of specialty 3D resins, is the first to produce a biocompatible 3D resin that’s “monomer-free.” This material complies with health and safety standards and are ideal for a variety of dental appliances, such as night guards, aligners, and drill guides. Other interesting resins from this manufacturer include fiber-reinforced resins and “two photon” resins for nano-scale 3D printing.
The value of biocompatible resins in dental 3D printing is given focus rarely. Biocompatible materials ensure the safety of dental appliance users. Thanks to biocompatible resins, orthodontists and dental professionals can create durable and effective custom dental appliances that patients can use without fear of toxic poisoning or other harmful effects.
